Construction of the case history multimodal format including a specialized module for the purposes of cardiology
An electronic case history (ECH) will constitute a universal tool for communication between various regional and reference medical centres which participate in the cardiological patient treatment process.
Projected ECH architecture:
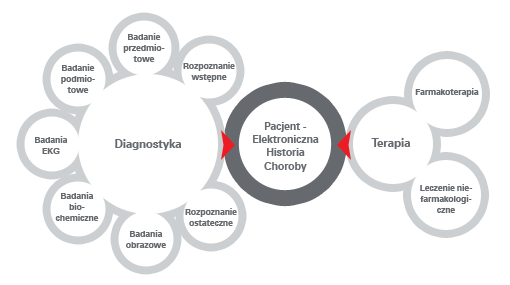
- Diagnostics
- initial diagnosis
- physical examination
- interview
- ECG examination
- biochemical examinations
- image examinations
- final diagnosis
- Therapy
- pharmacotherapy
- non-pharmacological treatment
Patient - electronic case history:
- routine diagnostic and therapeutical proceedings
- latest patient risk evaluation models
- diagnostic examinations and treatment forms compliant with the effective standards
System assumptions: - construction of an electronic case history
- collection and processing of metadata on the patient and his/her examinations
- construction of a database for multimodal data storage
- development of image data visualization tools
- development of a system of decision-making and risk assessment in acute coronary syndromes
IT tools used in the telemedical system: - application of the latest information technologies - grid technologies
- interfaces
- WWW
- applications used mainly as visual data analysis software
- open source/free software tools
- data security: cryptographic algorithms, HTPPS protocols, server mirroring, etc.
| 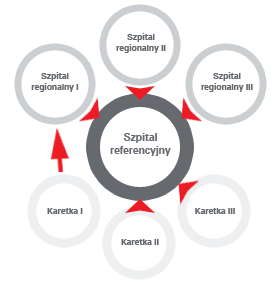 Telecardiological system structure |
Standards planned to be used in ECH.
The purpose of applying the standards is to achieve interoperability of different systems. Technological interoperability means that systems can exchange and use data. Semantic interoperability means that systems interpret data in the same way.
- HL7 (Health Level 7) - defines the principles of text data exchange in medicine by defining a communication system and message formats.
- DICOM - Digital Imaging and Communication in Medicine, i.e. RTG, USG, CT and MRI, etc.
- Clinical Document Architecture (CDA) – a HL7 v.3 family standard of multilayer architecture which is legible for a human and can be machine-processed.
- SNOMED CT - Systematized Nomenclature of Medicine - Clinical Terminology
- ICD-10 classification (International Classification of Diseases) - International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Health Problems - an international nosological diagnosis system. /li>
- XML - a standard for a universal text format to record data in the XML electronic form.
Data security in ECH:
- Transmission security - application of encrypted protocols to ensure the appropriate security level.
- Session tracking mechanism - a unique identifier is connected with a session; it is generated by means of cryptographic algorithms.
- Server failure protection - mirroring: a system of two servers operating as a mirror reflection - if one of the servers fails, the other takes over its functions.
Summary:
- The system can become a starting point for the development of telemedicine and the construction of state-of-the-art teleinformation systems on the Polish market in various health care areas.
- The applied standards should ensure interoperability of different systems.
- Integration of different encoding standards.
- Solutions should ensure a high data security level both in a database and during its teletransmission.