Sponsors
Idea
An acute coronary syndrome, including an infarction, is one of the major health problems in modern societies. Each year, approximately 100 thousand people suffer from a heart infarction in Poland. The first hours are crucial for the future of the patient. In this case, the critical factor is the time necessary for formulating a precise diagnosis and commencing a therapy. Every instance of shortening the duration of transport of a patient with an acute infarction to a PTCA (Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty) procedure by approximately 30 minutes reduces the 30-day death rate by approximately 15%. The subsidization obtained from the funds of the European Economic Area (EEA) Financial Mechanism and the Norwegian Financial Mechanism in the "Scientific Research" priority allowed the undertaking of the project of the development of the advanced methods of medical imaging, distributed acquisition, archiving and teletransmission in an integrated system of cardiological care of acute coronary syndromes. The project is carried out under the partnership cooperation of the teams of the University of Warsaw – the Interdisciplinary Centre for Mathematical and Computational Modelling and the Medical University of Warsaw – the 1st Department of Cardiology and the Department of Medical IT and Telemedicine and a Norwegian partner - Trollhetta AS. The objective of the project is to improve the quality of medical services by applying the latest IT developments in cardiology.
PartnersThe KARDIONET project is carried out thanks to the cooperation of the three institutions:
more about the project partners.. Tasks
JustificationThe most frequent cause of mortality in Poland (approx. 50% of all deaths) are cardiovascular diseases. Among all cardiovascular diseases, acute coronary syndromes prevail, including the three types of clinical events: a myocardial infarction, an unstable coronary disease, certain cases of a cardiac death. Estimated calculations give a number of approximately 250 000 cases in Poland per year. The application of an intervention cardiology procedure – coronary angioplasty is the most frequently used type of acute coronary syndrome treatment. This procedure is carried out only in cardiology centres of a high reference degree, e.g. academic centres in large towns. The success of the treatment depends on the time from the moment the symptoms occur to the moment the coronary artery patency is restored. That is why an efficient communication system between an ambulance and/or a low reference degree centre, e.g. a poviat hospital and a high reference degree centre carrying out an angioplasty procedure is of crucial importance. Innovative characterThe innovative character of the Kardionet project consists in the application of grid technologies. A grid is a system which integrates and manages the resources connected by a computer network and controlled by various domains and institutions. The grid technologies enable secure and fully controlled access to distributed data. The technologies also enable user authentication, creation of virtual organisations and comfortable and flexible usage of the resources. A part of the project is the creation of a uniform patient information system containing various diagnostic data, e.g. USG pictures or ECG graphs. Expected results
Cardiovascular diseases are the main cause of death in Poland. The elementary problem is too rare and little precise recognition of a cardiac insufficiency in the ambulatory and pre-hospital practice. More than 75% of cases are finally diagnosed as late as in hospital. The application of teleinformation solutions in the diagnostics which use visualisation techniques available in reference centres will enable formulation of a diagnosis in places other than a specialised hospital and the correct therapy can be undertaken before the patient arrives at the centre of destination. |


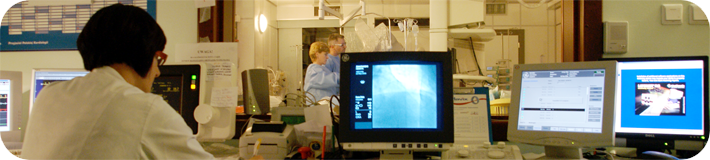

 KARDIONET is a system which integrates the advanced methods of medical imaging, distributed acquisition, archiving and teletransmission in an integrated system of cardiological care of acute coronary syndromes.
KARDIONET is a system which integrates the advanced methods of medical imaging, distributed acquisition, archiving and teletransmission in an integrated system of cardiological care of acute coronary syndromes.